
CT Signs of Urethral Injury RadioGraphics
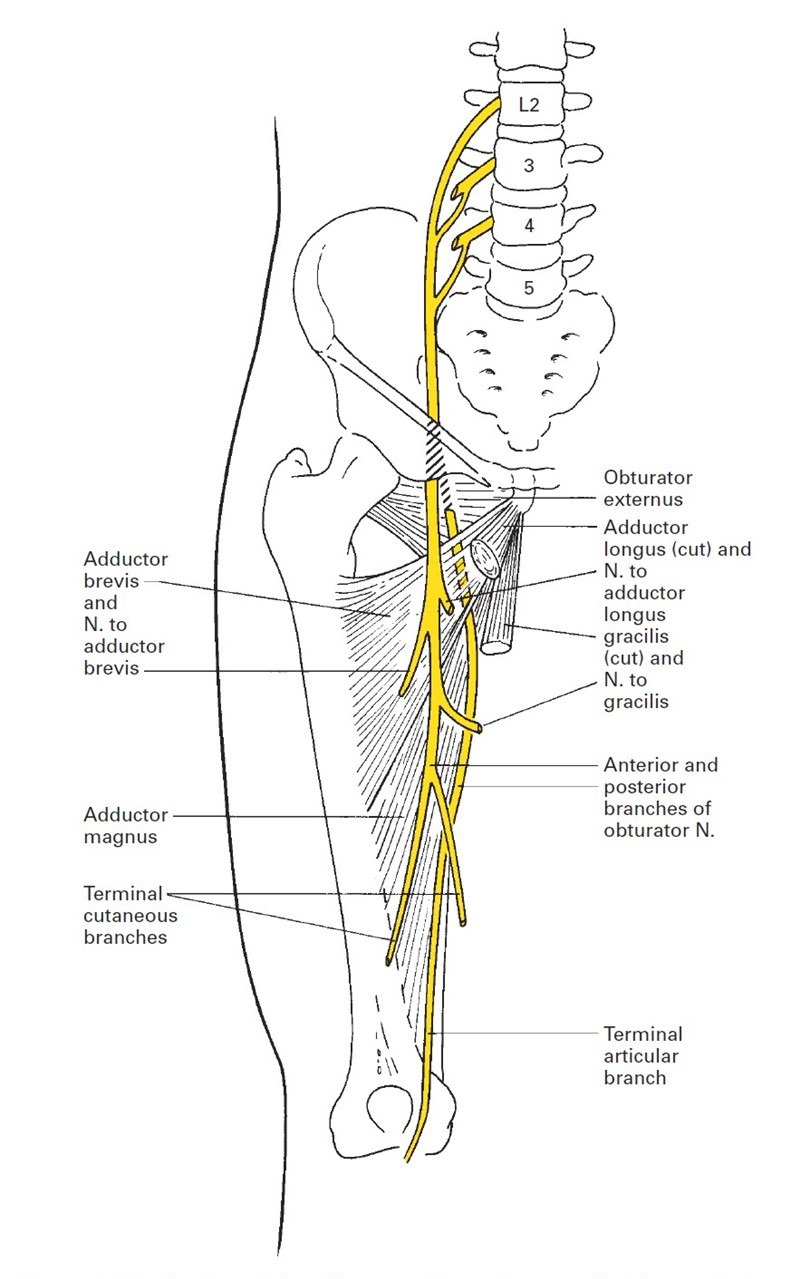
The obturator nerve is one of the largest branches of the lumbar plexus. It is a mixed nerve which arises from the ventral (anterior) rami of the spinal nerves L2-L4. The function of the obturator nerve is to provide motor innervation to all the medial muscles of the thigh (hip adductors) except for the ischiocondylar (hamstring) part of the.

obturator internus Diagram Quizlet
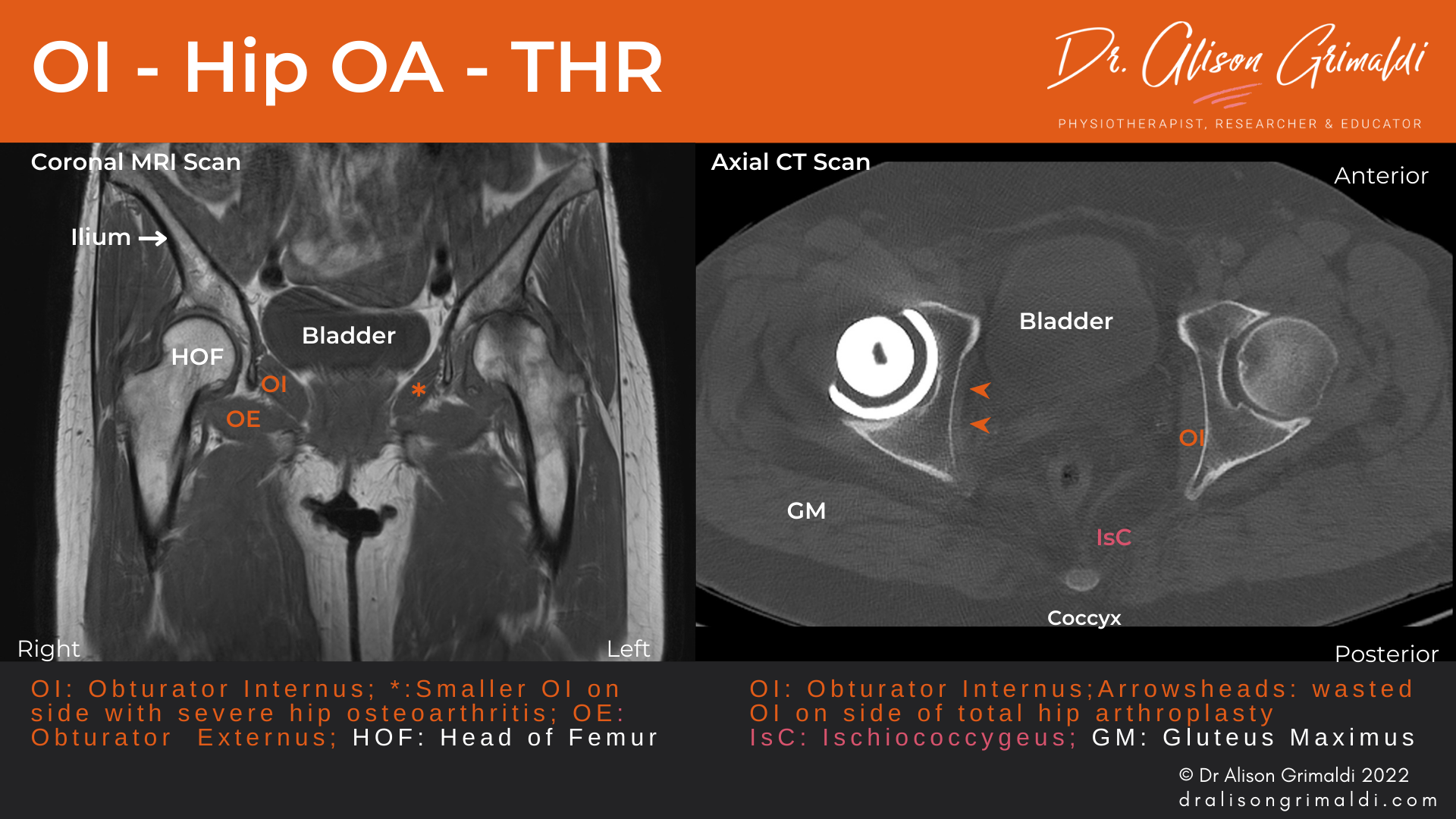
The fascia of the obturator internus muscle is medially related to the obturator artery and nerve, as they run anteroinferiorly from the anterior trunk on the lateral pelvic wall to the upper part of the obturator foramen.
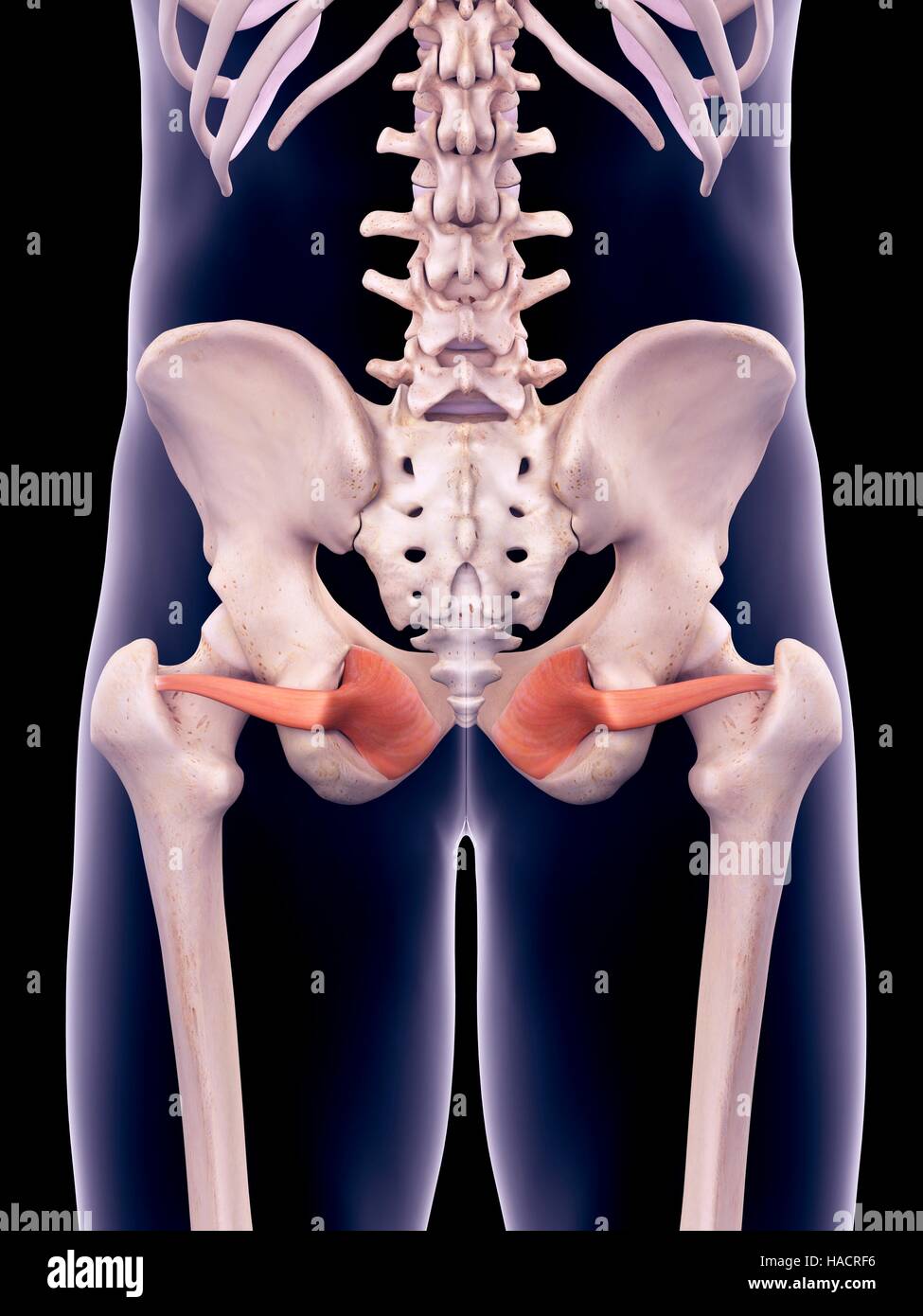
Abbildung der Obturator Internus Muskeln Stockfotografie Alamy
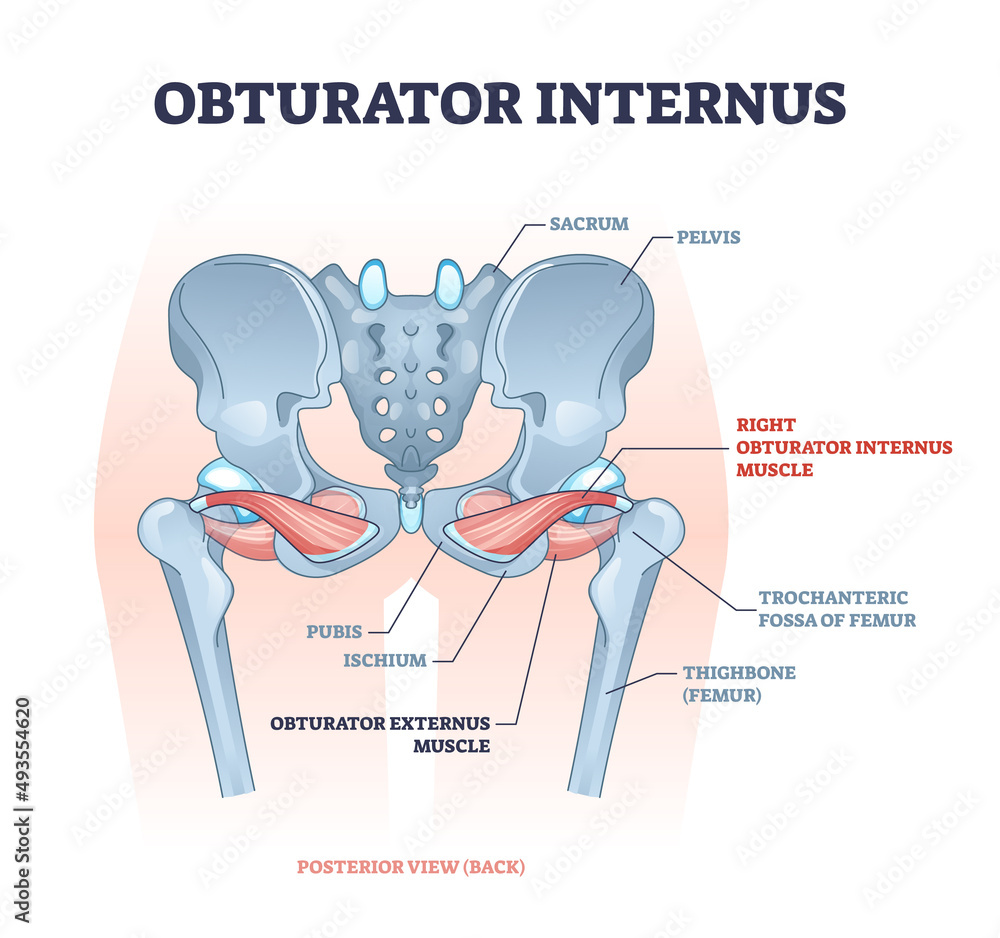
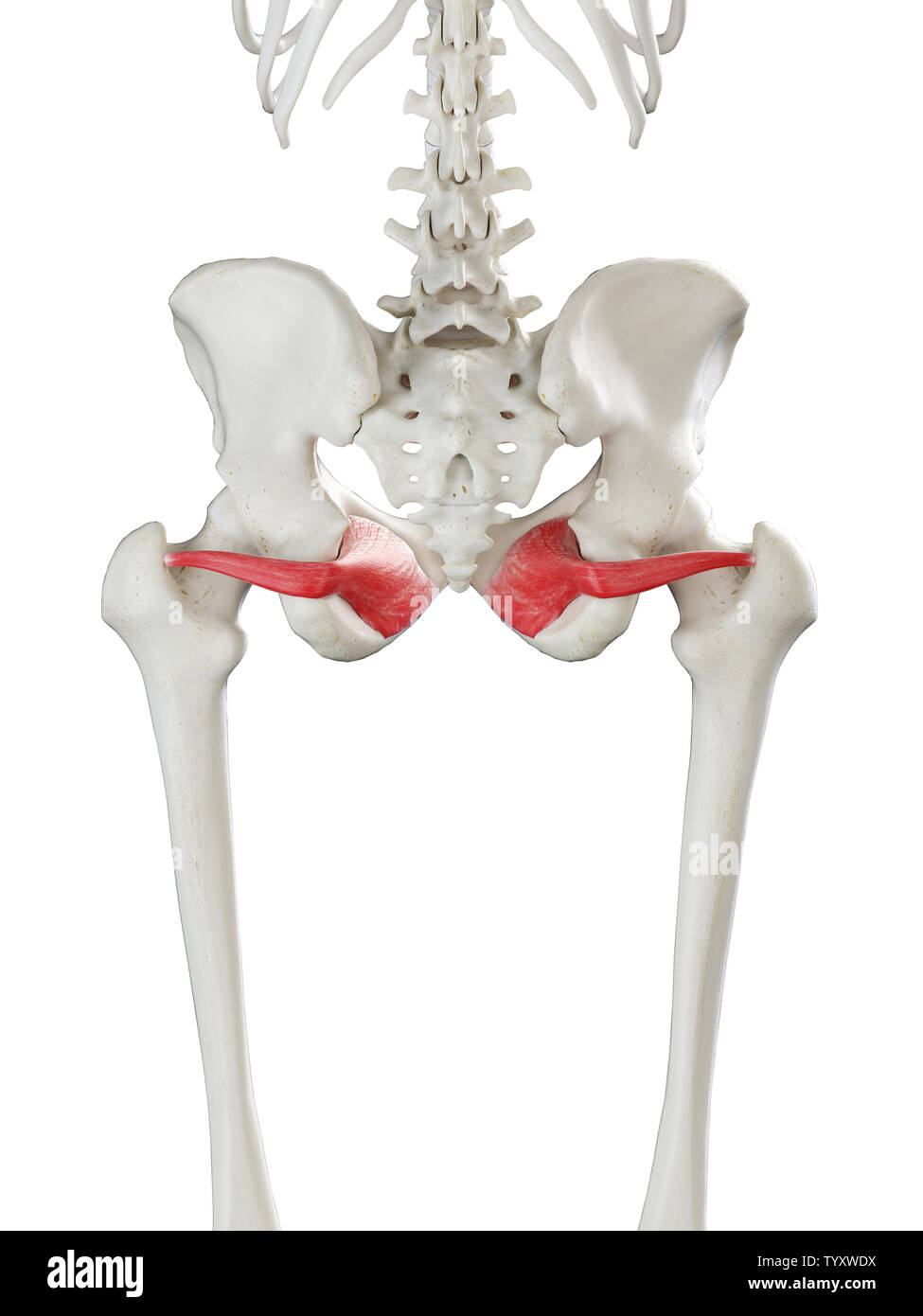
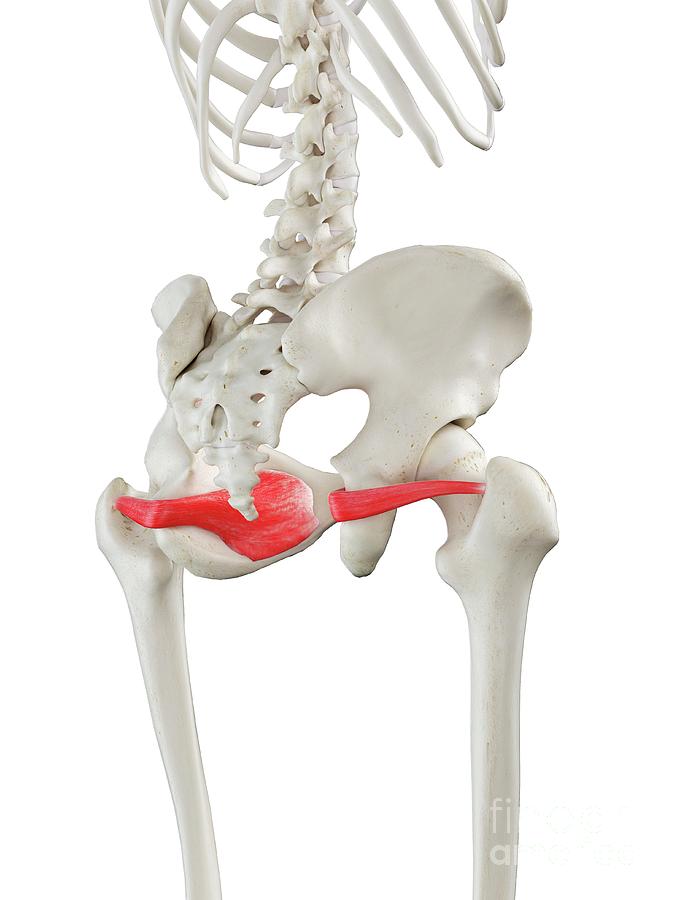
Obturator internus. Origin. Internal surface of obturator membrane and posterior bony margins of obturator foramen. Insertion. Medial surface of greater trochanter of femur, in common with superior and inferior gemelli. Action. Rotates the thigh laterally; also helps abduct the thigh when it is flexed. Innervation.
Obturatorius Fotos und Bildmaterial in hoher Auflösung Alamy
The word obturator comes from the Latin word obturo, which means "to stop or block up." This adequately illustrates the location of the obturator muscles since they cover the opening of the obturator foramen. Both the obturator externus and obturator internus are bilateral-triangular shaped muscles. Generally, they originate from the obturator membrane and pelvic bone and attach to the.

Obturator internus pyomyositis Emergency Medicine Journal
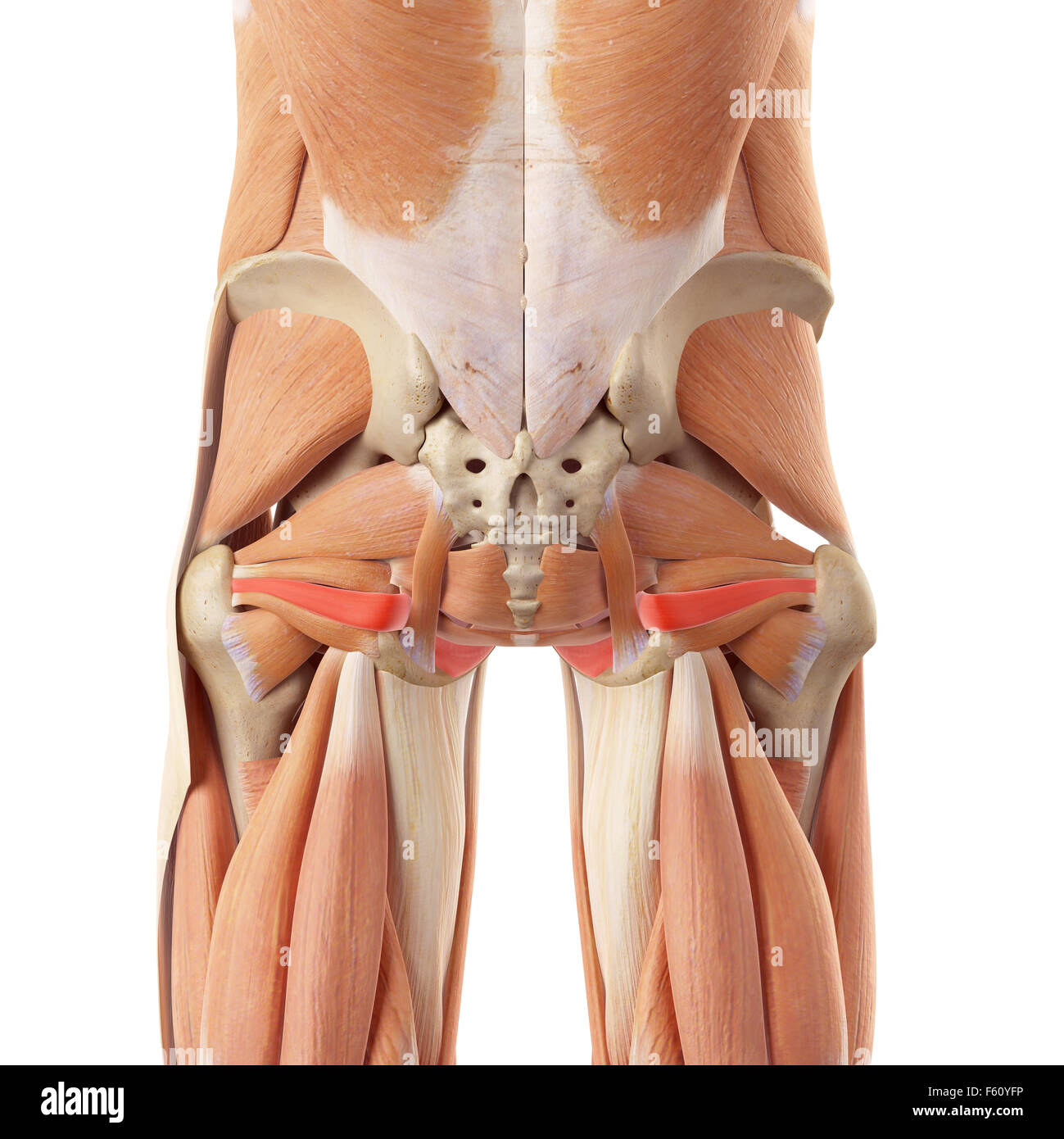
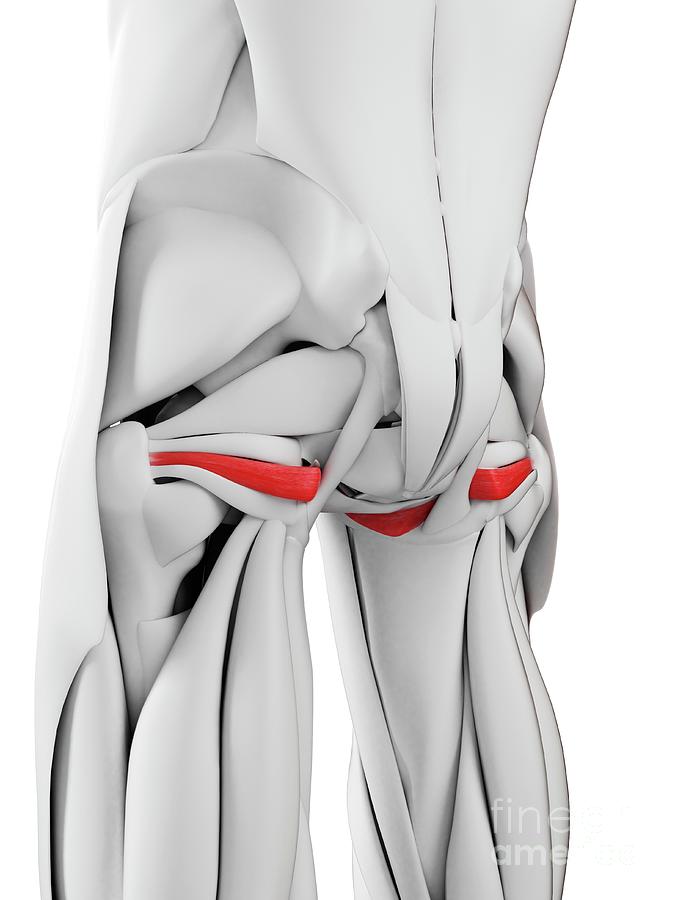
Obturator internus is a muscle that is situated deep to gluteus maximus, gluteus minimus, and gluteus medius in the gluteal region. It is one of six deep lateral hip rotators which aid in hip stabilization and movement when walking, running, and standing. Due to its function as a hip stabilizer, obturator internus is essential for preventing.

Meet the Obturator Internus — Southern Pelvic Health Physical Therapy
Obturator-internus-Syndrom: Ursache von Gesäßschmerzen Ohne Zuordnung (e) / Von Arotoky R. / 15/05/2022 Quelle Teilen Sie es mit Ihren besorgten Lieben 4.4 ( 12) Artikel überprüft und genehmigt von Dr. Ibtissama Boukas, Facharzt für Allgemeinmedizin Die perineale Schmerzen machen etwa 4 bis 5 % der Konsultationen in Schmerzzentren aus.

Meet the Obturator Internus — Southern Pelvic Health Physical Therapy
The obturator internus muscle originates from the inferior margin of the superior pubic ramus and from the pelvic surface of the obturator membrane. [1] Insertion Its tendon exits the pelvis through the lesser sciatic foramen to insert onto the greater trochanter of the femur. [1] Nerve
Obturator Internus Muscle Photograph by Sebastian Kaulitzki/science Photo Library Fine Art America
The nerve to obturator internus (also known as the obturator internus nerve [citation needed]) is a mixed (sensory and motor) nerve providing motor innervation to the obturator internus muscle and gemellus superior muscle, and sensory innervation to the hip joint. It is a branch of the sacral plexus.It is one of the group of deep gluteal nerves. It exits the pelvis through the greater sciatic.

Meet the Obturator Internus — Southern Pelvic Health Physical Therapy
The most affected muscles in traumatic groin pain syndrome are rectus abdominis, adductors, and iliopsoas. The internal obturator muscle lesion is very rare. The internal obturator muscle externally rotates the thigh and contributes to the stabilization of the hip joint and its indirect injury may cause the onset of traumatic groin pain syndrome.
:watermark(/images/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0)/images/anatomy_term/musculus-obturatorius-internus-6/QiT6ZMqyu74M9VdwndWg_Obturator_Internus_Muscle_01.png)
Obturator internus muscle (Musculus obturatorius internus) Kenhub
A small case series has described obturator internus muscle injury occurring alongside injury of other gluteal muscles after posterior hip dislocation secondary to trauma [4]. We describe 2 cases of obturator internus strain in high level young male athletes involved in kicking sports.
Obturator internus muscle with externus location near pelvis bone outline diagram. Labeled
Musculus obturator internus und Musculi gemelli. Sämtliche Sehnen dieser Muskeln und Schleimbeutel können im Bereich des Trochanter major entzünden und starke Hüftschmerzen hervorrufen. Man spricht auch vom Trochanter-major-Schmerzsyndrom. Dabei handelt es sich um eine weit verbreitete Ursache für Hüftschmerzen.
Obturator Internus Stockfotos und bilder Kaufen Alamy
The Obturator Internus fascia form's Alock's Canal, which houses the pudendal nerve and vessels. When this muscle becomes overactive or too tight symptoms of pudendal neuralgia can develop. People may feel shooting, stabbing, burning, or itching in the genitals, perineum, and/ or anus. Many people with OI dysfunction also have pelvic floor.
How I Do It Obturator Nerve Block
The obturator internus is a muscle of the gluteal region in the lower limb. It forms part of the lateral wall of the pelvic cavity. Attachments: Originates from the pubis and ischium at the obturator foramen.It travels through the lesser sciatic foramen and attaches onto the greater trochanter of the femur.
The hip and pelvic floor Let's get it together! Find out more
The obturator internus muscle originates from the inferior margin of the superior pubic ramus and from the pelvic surface of the obturator membrane. Its tendon exits the pelvis through the lesser sciatic foramen to insert onto the greater trochanter of the femur to laterally rotate the thigh. This muscle is innervated by the obturator internus.
Obturator Internus Muscle Photograph by Sebastian Kaulitzki/science Photo Library
The obturator nerve is a major peripheral nerve in your thigh. It's responsible for some leg movements (motor function) as well as sensation (sensory function). This nerve is formed by portions of the lumbar plexus, which is a complex network of nerves that emerge from the lumbar region of the spine, which is in your lower back.
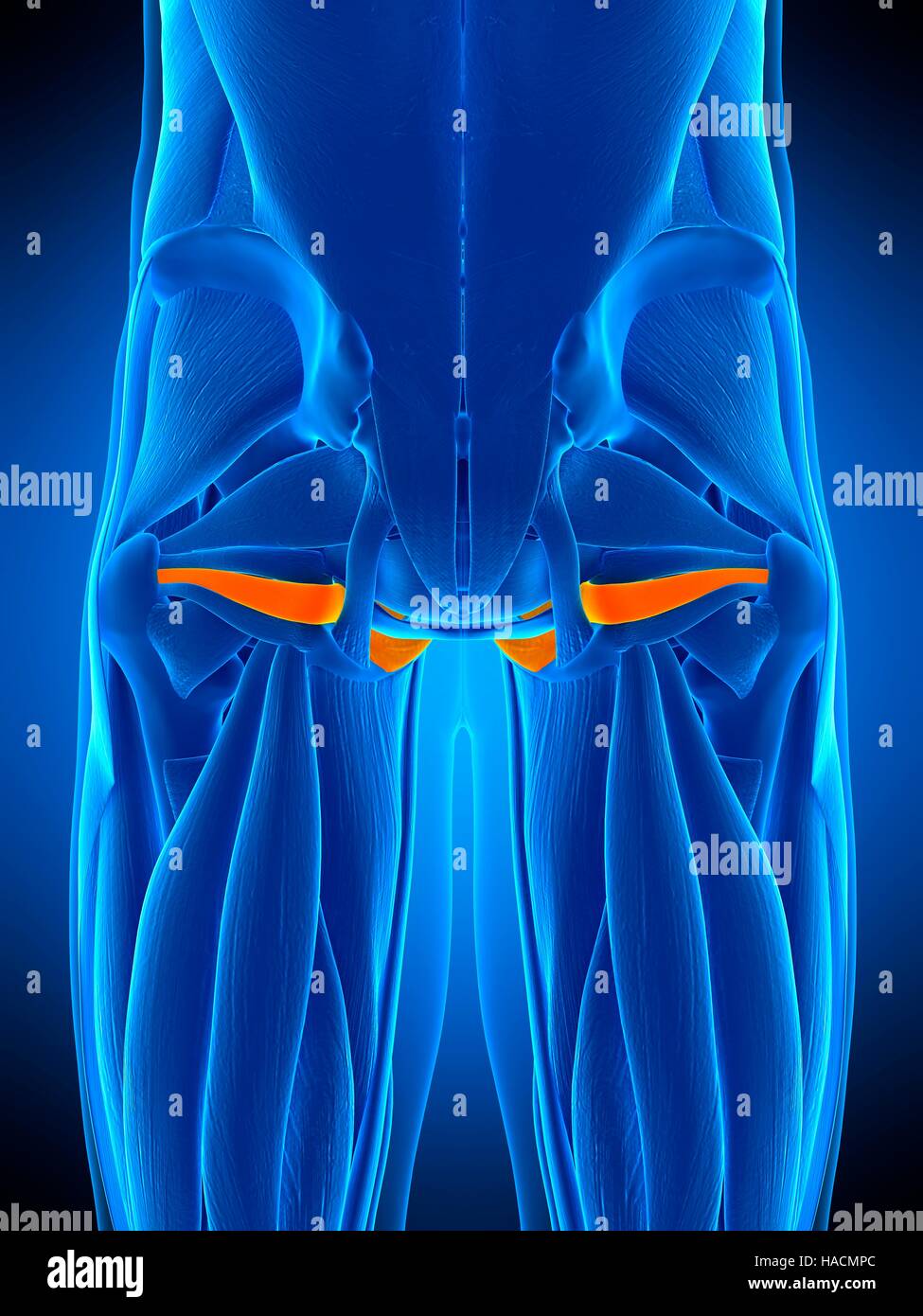
Illustration der Obturator Internus Muskel Stockfotografie Alamy
The obturator internus muscle, like the piriformis muscle, is both a muscle of the pelvic wall and of the gluteal region.It originates within the pelvis, and continues as a flattened tendon posteriorly through the lesser sciatic foramen (between ischial spine and tuberosity).. Summary. origin. anterolateral wall of true pelvis; deep surface of obturator membrane and pelvic surfaces of pubis.